 Blog's Page
Blog's Page
In The Ever-evolving Landscape Of Cyber-threats, Ransomware Remains One Of The Most Formidable Risks To Organisations And Individuals Alike. Among The Latest Entrants In This Arena Is The Ransomware Variant Known As Nobody Ransomware (also Stylised As NOBODY ransomware). First Identified In Late 2025, This Malicious Software Has Quickly Drawn Attention For Its Aggressive Behaviour, Broad File-targeting, And The High Pressure It Places On Victims To Pay.
ComputerSecurityInfo's Blog Post Provides A Comprehensive Exploration Of Nobody Ransomware: Its Characteristics, Infection Vectors, Encryption Process, Demands, And — Crucially — Guidance On Prevention, Detection, And Remediation. For Organisations And Users Wanting To Harden Their Defences Or Recover From An Attack, Understanding This Threat Is Essential.
Nobody Ransomware Is A Strain Of The Broader “Dharma/Chaos” Ransomware Family. Security Researchers Analysing Samples On Services Such As VirusTotal Found That It Acts As A Crypto-locker: Once Executed On A System It Encrypts Files, Appends A Unique Victim ID And A Random Four?character Extension (for Example, “.ckoz”, “.jylq”, Etc.) To Each Encrypted File, And Then Drops Ransom Notes Demanding Payment In Cryptocurrency.
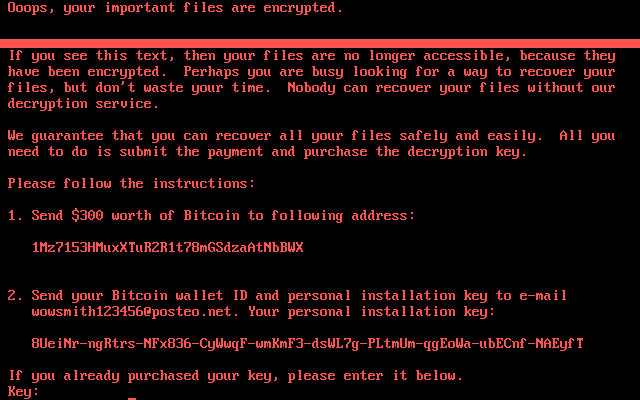
The Ransom Note Typically Includes Language Such As:
“NOBODY RANSOMWARE – Don’t Worry, You Can Return All Your Files! All Your Files Like Documents, Photos, Databases And Other Important Are Encrypted.”
It Then Offers To Decrypt Three Files For Free As A “guarantee”, Before Demanding Payment (commonly In Bitcoin) And Instructing Victims To Contact Via A Specified Telegram Handle.
While Many Ransomware Campaigns Target Specific Large Organisations, Nobody Appears To Focus On Infecting A Broad Range Of File Types, Including Not Just Personal Documents And Media But Also Backups, Databases, And Network Shares.
By Appending Random Extensions And Generating Unique Victim Identifiers, And By Seeking To Disable Recovery Mechanisms Like Volume Shadow Copies, The Attackers Behind Nobody Aim To Maximise Pressure.
Understanding How Nobody Enters Systems Is Key To Prevention. According To Cybersecurity Analysts, Typical Vectors Include:
Once The Malware Gains A Foothold, It Often Executes The Following Sequence: Terminate Key Processes, Enumerate Drives And Network Shares, Append Victim Identifiers And Random Extensions To Filenames, Encrypt Data, Delete Or Disable Backups (e.g., VSS Shadow Copies), Drop Ransom Notes In Folders, And Change Desktop Wallpaper To Reinforce The Demand.
An Interesting Tactic Flagged By Researchers: Nobody May Perform Geo-IP Checks To Avoid Encrypting Systems In Regions Where Ransom Payments Are Unlikely, Thereby Optimising Its “business Model”.
The Core Mechanism Of Nobody Ransomware Follows Established Ransomware-as-a-service Strategies, But With Some Notable Features:
Victims Are Urged To Contact A Telegram Account (or An Email) And Instructed To Pay To Regain Access. The Same Note Leverages Psychological Pressure — Implying That Failure To Pay May Result In Permanent Data Loss. The Random Extension Makes It Difficult To Ignore Or Bypass The Encryption Without A Decryption Key.
The Implications Of A Nobody Ransomware Infection Are Severe, Especially In Business Environments. Key Impacts Include:
In Short, The Arrival Of Nobody Ransomware Underscores How Even Less Well-known Ransomware Variants Can Deliver High Damage. Ignoring “smaller” Strains Is A Dangerous Gamble.
Early Detection Is Critical To Limiting Damage. Here Are Telltale Signs That Nobody Ransomware May Be Operating In Your Environment:
If You Observe These Signs, Immediate Incident Response Is Required: Isolate Affected Systems, Disconnect From Networks, Engage Forensic/security Specialists, And Assess Backup Integrity.
The Most Effective Strategy Against Nobody Ransomware — And Ransomware Generally — Is Prevention. Some Key Safeguards Include:
Taking These Measures Gives The Best Chance Of Either Preventing An Infection Entirely Or Significantly Limiting Its Impact.
Despite Best Efforts, Infections May Still Occur. If You Believe You Are Impacted By Nobody Ransomware, Follow These Steps:
1. Isolate The Infected System(s) Immediately By Disconnecting From Networks And Disabling Shared Drives Or Cloud Sync For Those Devices.
2. Preserve Forensic Evidence: Do Not Reboot Or Shut Down Systems Unless Absolutely Necessary; Capture Memory And Disk Images If Possible, And Log Relevant Events.
3. Assess Backup Integrity: Are Backups Available? Are They Intact And Ransomware-free? If Yes, You May Be Able To Restore Without Paying.
4. Do Not pay The Ransom As A First Resort: Paying Does Not Guarantee Decryption, And May Encourage Further Attacks. Security Guidance Strongly Advises Caution.
5. Consult With Cybersecurity Professionals Or Law-enforcement: They Can Help With Decryption Research, Negotiating, And Containment.
6. Remove The Malware: Use Reputable Anti-malware Tools Or Engage A Specialist To Eradicate The Ransomware And Its Components (so It Doesn’t Reinfect After Recovery).
7. Restore From Backups: If Viable, Format Affected Systems And Restore From Clean Backups. Verify Integrity And Safety Of Restored Files.
8. Post-mortem & Hardening: Investigate Root Cause (how The Infection Occurred), Strengthen Defences, Patch Gaps, Update Policies And Conduct Training To Prevent Recurrence.
Even With Thorough Response, Recovery Can Be Costly And Disruptive — A Powerful Reminder Of Why Prevention Is Preferable.
You Might Wonder: “Why Focus On This Particular Strain?” There Are Several Reasons:
In Essence, If You Treat Ransomware As A “someone Else’s Problem”, You May Be Caught Off-guard. Nobody Ransomware Is One More Reason To Take Ransomware Risk Seriously.
The Arrival Of The Nobody Ransomware Variant Underscores The Harsh Reality That No Device, System Or Organisation Is Immune. Whether You Manage A Corporate IT Infrastructure Or Run A Small Business (or Even Just Use A Personal Computer), The Threat Is Real, Present And Evolving. Because Nobody Uses Strong Encryption, Broad File Targeting, And Aggressive Tactics (like Deleting Backups), Your Best Bet Lies In prevention, detection, And recovery Preparedness.
A Focused Strategy Combining User Education, Robust Backups, Patching, Segmentation, Endpoint Monitoring And An Incident Response Plan Offers The Best Defence. If You Do Encounter An Infection, Fast Isolation, Forensic Triage, And Disciplined Recovery Are Essential. Most Importantly: Do not rely On Paying The Ransom As A Fallback.
By Staying Informed About Emerging Strains Like Nobody Ransomware, And Taking Proactive Steps Today, You Can Reduce Your Risk Of Becoming The Next Victim. The Cost Of Preparation Is Far Less Than The Cost Of Remediation — And Remembering That “nobody” Should Be Replacing your files Is The Last Thing You Want.
Step 1: Boot Into Safe Mode
Restart Your PC And Press F8 (or Shift + F8 For Some Systems) Before Windows Loads.
Choose Safe Mode With Networking.
Safe Mode Prevents Most Malware From Loading.
Press Win + R, Type appwiz.cpl, And Press Enter.
Sort By Install Date And Uninstall Unknown Or Recently Added Programs.
Use A Trusted Anti-malware Tool:
Malwarebytes – https://www.malwarebytes.com
Screenshot Of Malwarebytes - Visit Links
Microsoft Defender – Built Into Windows 10/11
HitmanPro, ESET Online Scanner, Or Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool
ZoneAlarm Pro Antivirus + Firewall NextGen
VIPRE Antivirus - US And Others Countries, | India
Run A Full Scan And Delete/quarantine Detected Threats.
Win + R, Type temp → Delete All Files.Press Win + R, Type %temp% → Delete All Files.
Use Disk Cleanup: cleanmgr In The Run Dialog.
Go To: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
Open hosts File With Notepad.
Replace With Default Content:
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc → Open Task Manager
Go To Startup Tab
Disable Any Suspicious Entries.
Open Command Prompt As Administrator.
Run These Commands:
netsh Winsock Reset
netsh Int Ip Reset
ipconfig /flushdns
Unwanted Homepage Or Search Engine
Pop-ups Or Redirects
Unknown Extensions Installed
For Chrome:
Go To: chrome://extensions/
Remove Anything Unfamiliar
For Firefox:
Go To: about:addons → Extensions
Remove Suspicious Add-ons
For Edge:
Go To: edge://extensions/
Uninstall Unknown Add-ons
Chrome:
Go To chrome://settings/reset → "Restore Settings To Their Original Defaults"
Firefox:
Go To about:support → "Refresh Firefox"
Edge:
Go To edge://settings/resetProfileSettings → "Reset Settings"
All Browsers:
Use Ctrl + Shift + Del → Select All Time
Clear Cookies, Cached Files, And Site Data
Make Sure They Are Not Hijacked.
Chrome: chrome://settings/search
Firefox: about:preferences#search
Edge: edge://settings/search
Chrome: chrome://settings/cleanup
Use Malwarebytes Browser Guard For Real-time Browser Protection.
Always Download Software From Trusted Sources.
Keep Windows, Browsers, And Antivirus Updated.
Avoid Clicking Suspicious Links Or Ads.
Use ad Blockers And reputable Antivirus Software.
Backup Your Files Regularly.
To Remove Malware From Your Windows PC, Start By Booting Into Safe Mode, Uninstalling Suspicious Programs, And Scanning With Trusted Anti-malware Tools Like Malwarebytes. Clear Temporary Files, Reset Your Network Settings, And Check Startup Apps For Anything Unusual.
For web Browsers, Remove Unwanted Extensions, Reset Browser Settings, Clear Cache And Cookies, And Ensure Your Homepage And Search Engine Haven’t Been Hijacked. Use Cleanup Tools Like Chrome Cleanup Or Browser Guard For Added Protection.
?? Prevention Tips: Keep Software Updated, Avoid Suspicious Downloads, And Use Antivirus Protection Plus Browser Ad Blockers. Regular Backups Are Essential.
Why It Matters: Not All VPNs Offer Malware Protection.
What To Look For: Providers With built-in Malware/ad/tracker Blockers (e.g., NordVPN’s Threat Protection, ProtonVPN’s NetShield).
Purpose: Prevents Data Leaks If Your VPN Connection Drops.
Benefit: Ensures Your Real IP And Browsing Activity Aren’t Exposed To Malware-distributing Websites.
Why It Matters: DNS Leaks Can Expose Your Online Activity To Attackers.
Solution: Enable DNS Leak Protection In Your VPN Settings Or Use A Secure DNS Like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
Risk: Free VPNs Often Contain Malware, Sell User Data, Or Lack Security Features.
Better Option: Use Reputable Paid VPNs That Offer security Audits And Transparent Privacy Policies.
Some VPNs Block Known Phishing And Malicious Sites.
Example: Surfshark’s CleanWeb, CyberGhost’s Content Blocker.
Reason: Security Patches Fix Known Vulnerabilities.
Tip: Enable Auto-updates Or Check For Updates Weekly.
Scope: Malware Can Enter Through Phones, Tablets, Or IoT Devices.
Solution: Install VPN Apps On Every Internet-connected Device.
Fact: VPNs Do Not Remove Or Detect Malware On Your System.
Complement It With:
Antivirus Software
Firewall
Browser Extensions For Script Blocking
VPN Encrypts Traffic But Can’t Stop Malware From Executing If You Download Infected Files.
Split Tunneling Allows Certain Apps/sites To Bypass VPN.
Tip: Never Exclude Browsers, Email Clients, Or Download Managers From VPN Tunneling.
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) Enhances Your Online Privacy By Encrypting Your Internet Traffic And Masking Your IP Address. It Protects Your Data On Public Wi-Fi, Hides Browsing Activity From Hackers And ISPs, And Helps Bypass Geo-restrictions. VPNs Also Add A Layer Of Defense Against Malware By Blocking Malicious Websites And Trackers When Using Advanced Features. However, A VPN Does Not Remove Existing Malware Or Act As Antivirus Software. For Full Protection, Combine VPN Use With Antivirus Tools, Regular Software Updates, And Cautious Browsing Habits. Always Choose A Reputable VPN Provider With Strong Security And Privacy Policies.
Nobody Ransomware Remove Nobody Ransomware, Delete Nobody Ransomware, Get Rid Of Nobody Ransomware, Nobody Ransomware Removal Guide, How To Uninstall