 Blog's Page
Blog's Page
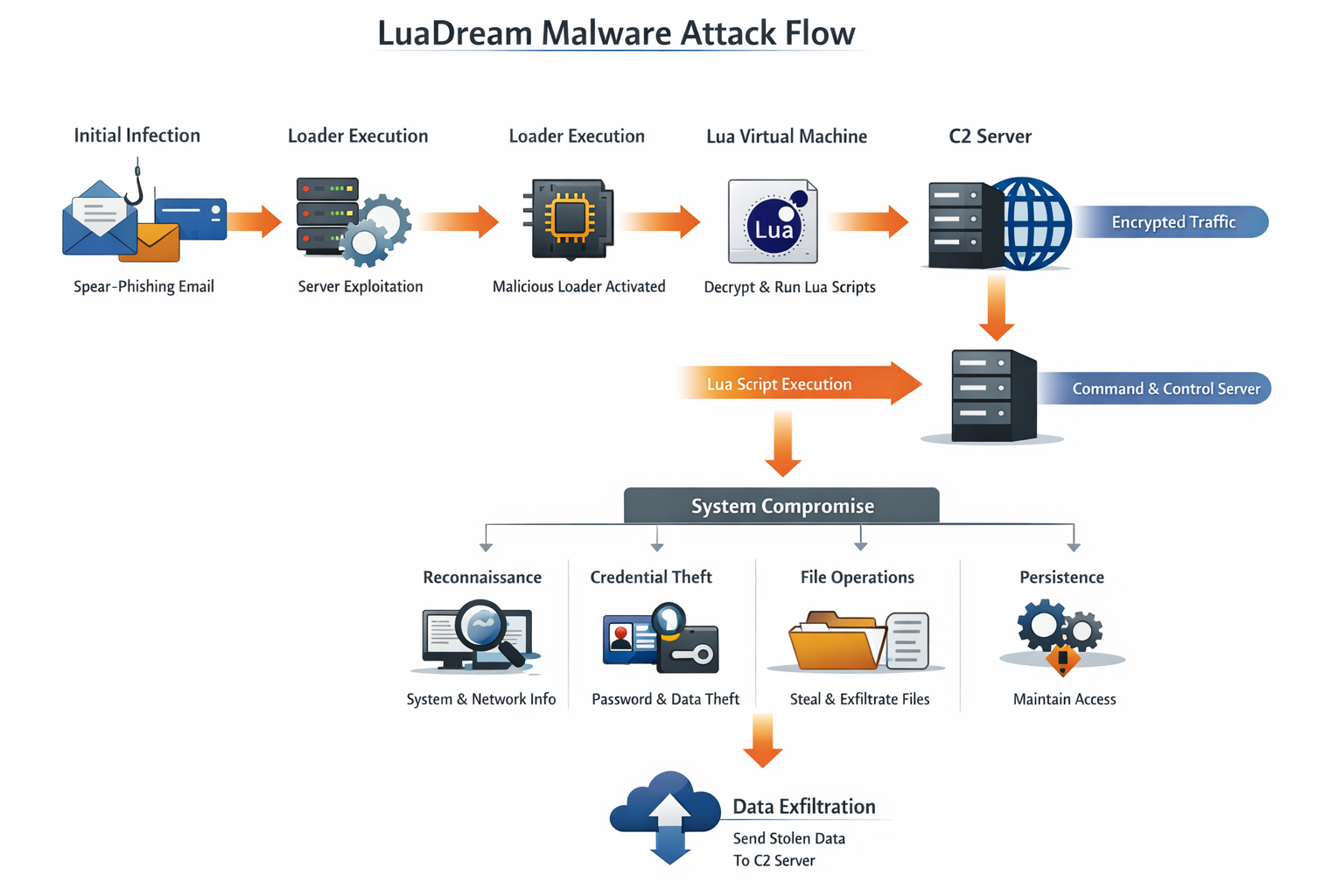
LuaDream Malware Is A sophisticated Cyber-espionage Backdoor That Has Gained Attention In The Cybersecurity Community Due To Its stealthy Behavior, Modular Design, And Use Of The Lua Scripting Language. Unlike Conventional Malware Written In C, C++, Or Python, LuaDream Leverages Lua To Dynamically Execute Malicious Logic, Making Detection And Analysis Significantly More Difficult. This Malware Is Primarily Associated With advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Activities, Targeting Government Institutions, Diplomatic Organizations, Telecommunications Providers, And High-value Enterprises.
LuaDream Is Designed For long-term Persistence And Covert Data Exfiltration, Indicating That Its Operators Are Not Financially Motivated Cybercriminals, But Rather nation-state–level Threat Actors Or Highly Organized Cyber-espionage Groups. The Malware’s Architecture Allows Attackers To Deploy New Capabilities Without Recompiling Binaries, Giving LuaDream Exceptional Flexibility In Real-world Attacks.
LuaDream Is A remote Access Trojan (RAT) And Cyber-espionage Backdoor That Enables Attackers To:
Maintain Persistent Access To Compromised Systems
Execute Arbitrary Commands Remotely
Download And Execute Additional Payloads
Exfiltrate Sensitive Data Covertly
Monitor User Activity And System Information
The Defining Characteristic Of LuaDream Malware Is Its embedded Lua Virtual Machine, Which Interprets Encrypted Lua Scripts Delivered From Command-and-control (C2) Servers. This Scripting-based Execution Model Allows The Malware To Evolve Dynamically, Evade Signature-based Detection, And Adapt To Different Target Environments.

The Use Of The Lua Programming Language Is A Strategic Choice By The Attackers. Lua Offers Several Advantages For Malware Developers:
Lightweight And Fast Execution
Cross-platform Compatibility
Dynamic Script Loading
Easy Obfuscation And Encryption
Low Detection Rates By Traditional Antivirus Engines
Because Most Security Products Focus On Detecting Malicious Binaries Rather Than Interpreted Scripts, LuaDream’s Lua-based Payloads Often Bypass Static Analysis Tools And Remain Undetected For Extended Periods.
LuaDream Is Widely Believed To Be Linked To A Chinese-speaking APT Group, Based On:
Overlapping Infrastructure With Other Known Espionage Campaigns
Similarities In Coding Style And Command Structure
Targeting Patterns Aligned With Geopolitical Intelligence Objectives
Although No Official Attribution Has Been Confirmed Publicly, LuaDream Shares Operational Similarities With Other Advanced Cyber-espionage Frameworks Used In state-sponsored Intelligence Gathering Operations.
LuaDream Malware Is Typically Deployed Through targeted Intrusion Techniques Rather Than Mass Infection Campaigns. Common Infection Vectors Include:
Highly Customized Phishing Emails Containing:
Malicious Attachments (ZIP, RAR, DOCX, PDF)
Weaponized Exploits
Links To Compromised Websites
Attackers Exploit Vulnerabilities In:
Web Servers
VPN Appliances
Email Servers
Network Management Interfaces
Malicious Code Is Injected Into:
Legitimate Software Installers
Updates From Compromised Vendors
Shared Internal Tools
Once Inside A Network, LuaDream May Be Deployed Through:
Stolen Credentials
Pass-the-hash Attacks
SMB Or RDP Exploitation
LuaDream Follows A multi-layered Modular Architecture, Designed For Stealth And Adaptability.
The Initial Loader Is A Small Native Executable That:
Establishes Persistence
Injects Itself Into Legitimate Processes
Loads The Embedded Lua Interpreter
The Embedded Lua VM:
Decrypts And Executes Lua Scripts
Allows Dynamic Command Execution
Enables Modular Payload Delivery
The Backdoor Provides:
Remote Command Execution
File System Access
Process Management
System Reconnaissance
LuaDream Supports Plugins For:
Credential Harvesting
Keylogging
Network Scanning
Data Exfiltration

LuaDream Communicates With Its C2 Servers Using custom Encrypted Protocols, Often Over Standard Ports Such As HTTP (80) And HTTPS (443). This Makes Its Traffic Blend Seamlessly With Legitimate Network Activity.
Encrypted Payload Delivery
Periodic Beaconing
Domain Rotation And Fast-flux DNS
Hard-coded Fallback Servers
The Malware Often Retrieves Lua Scripts From The C2 Server, Executes Them In Memory, And Returns The Output Without Writing Files To Disk.
LuaDream Employs Multiple Persistence Techniques To Survive Reboots And System Updates:
Registry Run Keys
Scheduled Tasks
DLL Hijacking
Service Installation
Startup Folder Abuse
Advanced Versions May Also Use boot-level Persistence Or fileless Execution To Reduce Forensic Traces.
LuaDream Provides Attackers With A Full Suite Of Espionage Capabilities:
OS Version And Architecture
Installed Software
Network Configuration
User Privileges
Upload, Download, Delete Files
Search For Sensitive Documents
Compress And Encrypt Stolen Data
Start Or Terminate Processes
Inject Code Into Running Applications
Browser Credential Harvesting
Memory Scraping
Access Token Theft
Encrypted Outbound Traffic
Steganographic Techniques
Chunked Data Transfer

LuaDream Is Specifically Engineered To Evade Detection And Forensic Analysis:
Encrypted Strings And Payloads
Runtime Decryption Of Lua Scripts
Anti-debugging Checks
Anti-sandbox Techniques
Fileless Execution
The Malware Often Disables Or Bypasses Security Tools Silently, Allowing It To Remain Hidden For Months Or Even Years.
The Impact Of A LuaDream Infection Can Be Severe, Especially For High-value Targets:
Theft Of Classified Or Confidential Information
Long-term Surveillance Of Internal Communications
Intellectual Property Loss
Compromise Of National Security Assets
Reputational And Financial Damage
Because LuaDream Is Used In Espionage Campaigns, Victims Often Remain Unaware Of The Compromise Until Extensive Damage Has Already Occurred.
Detecting LuaDream Malware Is Particularly Difficult Due To:
Lack Of Malicious Files On Disk
Use Of Legitimate System Processes
Encrypted And Obfuscated Lua Scripts
Low Behavioral Footprint
Traditional Antivirus Solutions Often Fail To Detect LuaDream Without advanced Behavioral Analysis And Threat Intelligence Integration.
Common Indicators Include:
Suspicious Outbound Connections To Unknown Domains
Unusual Lua Interpreter Activity
Registry Modifications Without User Action
Unexpected Scheduled Tasks
Encrypted Network Traffic Patterns
Organizations Should Use endpoint Detection And Response (EDR) Tools To Identify Such Anomalies.
Monitor Outbound Traffic
Block Suspicious Domains
Use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Deploy Advanced EDR/XDR Solutions
Enable Memory Scanning
Monitor Script Execution Behavior
Use Advanced Phishing Protection
Disable Macros By Default
Train Users On Spear-phishing Awareness
Regularly Update Systems And Software
Patch Public-facing Services Promptly
Perform Proactive Threat Hunting
Analyze Logs For Anomalous Behavior
If LuaDream Malware Is Suspected:
Isolate Affected Systems Immediately
Capture Memory Dumps For Forensic Analysis
Identify Persistence Mechanisms
Reset Compromised Credentials
Rebuild Systems From Trusted Backups
Due To LuaDream’s Stealthy Nature, full System Reimaging Is Often Recommended.
| Feature | LuaDream Malware | Traditional Backdoors |
|---|---|---|
| Language | Lua-based Scripting | C/C++ |
| Detection | Very Difficult | Moderate |
| Modularity | High | Limited |
| Fileless Execution | Yes | Rare |
| APT Usage | Common | Less Frequent |
LuaDream Represents A new Generation Of Malware Frameworks That Prioritize Stealth, Adaptability, And Long-term Intelligence Collection. Its Use Of Lua Scripting, Modular Design, And Encrypted Communication Makes It One Of The Most Challenging Threats To Detect And Mitigate.
For Governments, Enterprises, And Research Institutions, LuaDream Is Not Just Malware—it Is A strategic Cyber-weapon Designed For Silent Infiltration And Persistent Surveillance.
LuaDream Malware Is A highly Advanced Cyber-espionage Backdoor That Demonstrates How Modern Attackers Are Evolving Beyond Traditional Malware Techniques. By Combining Lua Scripting, Modular Payload Delivery, And Stealthy Persistence, LuaDream Poses A Significant Threat To Critical Infrastructure And Sensitive Organizations Worldwide.
To Defend Against Such Threats, Organizations Must Adopt advanced Security Architectures, Invest In continuous Monitoring, And Prioritize threat Intelligence–driven Defense Strategies. As Cyber-espionage Campaigns Continue To Grow In Sophistication, Understanding Threats Like LuaDream Is Essential For Building Resilient Cybersecurity Defenses.
Step 1: Boot Into Safe Mode
Restart Your PC And Press F8 (or Shift + F8 For Some Systems) Before Windows Loads.
Choose Safe Mode With Networking.
Safe Mode Prevents Most Malware From Loading.
Press Win + R, Type appwiz.cpl, And Press Enter.
Sort By Install Date And Uninstall Unknown Or Recently Added Programs.
Use A Trusted Anti-malware Tool:
Malwarebytes – https://www.malwarebytes.com
Screenshot Of Malwarebytes - Visit Links
Microsoft Defender – Built Into Windows 10/11
HitmanPro, ESET Online Scanner, Or Kaspersky Virus Removal Tool
ZoneAlarm Pro Antivirus + Firewall NextGen
VIPRE Antivirus - US And Others Countries, | India
Run A Full Scan And Delete/quarantine Detected Threats.
Win + R, Type temp → Delete All Files.Press Win + R, Type %temp% → Delete All Files.
Use Disk Cleanup: cleanmgr In The Run Dialog.
Go To: C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
Open hosts File With Notepad.
Replace With Default Content:
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc → Open Task Manager
Go To Startup Tab
Disable Any Suspicious Entries.
Open Command Prompt As Administrator.
Run These Commands:
netsh Winsock Reset
netsh Int Ip Reset
ipconfig /flushdns
Unwanted Homepage Or Search Engine
Pop-ups Or Redirects
Unknown Extensions Installed
For Chrome:
Go To: chrome://extensions/
Remove Anything Unfamiliar
For Firefox:
Go To: about:addons → Extensions
Remove Suspicious Add-ons
For Edge:
Go To: edge://extensions/
Uninstall Unknown Add-ons
Chrome:
Go To chrome://settings/reset → "Restore Settings To Their Original Defaults"
Firefox:
Go To about:support → "Refresh Firefox"
Edge:
Go To edge://settings/resetProfileSettings → "Reset Settings"
All Browsers:
Use Ctrl + Shift + Del → Select All Time
Clear Cookies, Cached Files, And Site Data
Make Sure They Are Not Hijacked.
Chrome: chrome://settings/search
Firefox: about:preferences#search
Edge: edge://settings/search
Chrome: chrome://settings/cleanup
Use Malwarebytes Browser Guard For Real-time Browser Protection.
Always Download Software From Trusted Sources.
Keep Windows, Browsers, And Antivirus Updated.
Avoid Clicking Suspicious Links Or Ads.
Use ad Blockers And reputable Antivirus Software.
Backup Your Files Regularly.
To Remove Malware From Your Windows PC, Start By Booting Into Safe Mode, Uninstalling Suspicious Programs, And Scanning With Trusted Anti-malware Tools Like Malwarebytes. Clear Temporary Files, Reset Your Network Settings, And Check Startup Apps For Anything Unusual.
For web Browsers, Remove Unwanted Extensions, Reset Browser Settings, Clear Cache And Cookies, And Ensure Your Homepage And Search Engine Haven’t Been Hijacked. Use Cleanup Tools Like Chrome Cleanup Or Browser Guard For Added Protection.
?? Prevention Tips: Keep Software Updated, Avoid Suspicious Downloads, And Use Antivirus Protection Plus Browser Ad Blockers. Regular Backups Are Essential.
Why It Matters: Not All VPNs Offer Malware Protection.
What To Look For: Providers With built-in Malware/ad/tracker Blockers (e.g., NordVPN’s Threat Protection, ProtonVPN’s NetShield).
Purpose: Prevents Data Leaks If Your VPN Connection Drops.
Benefit: Ensures Your Real IP And Browsing Activity Aren’t Exposed To Malware-distributing Websites.
Why It Matters: DNS Leaks Can Expose Your Online Activity To Attackers.
Solution: Enable DNS Leak Protection In Your VPN Settings Or Use A Secure DNS Like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1).
Risk: Free VPNs Often Contain Malware, Sell User Data, Or Lack Security Features.
Better Option: Use Reputable Paid VPNs That Offer security Audits And Transparent Privacy Policies.
Some VPNs Block Known Phishing And Malicious Sites.
Example: Surfshark’s CleanWeb, CyberGhost’s Content Blocker.
Reason: Security Patches Fix Known Vulnerabilities.
Tip: Enable Auto-updates Or Check For Updates Weekly.
Scope: Malware Can Enter Through Phones, Tablets, Or IoT Devices.
Solution: Install VPN Apps On Every Internet-connected Device.
Fact: VPNs Do Not Remove Or Detect Malware On Your System.
Complement It With:
Antivirus Software
Firewall
Browser Extensions For Script Blocking
VPN Encrypts Traffic But Can’t Stop Malware From Executing If You Download Infected Files.
Split Tunneling Allows Certain Apps/sites To Bypass VPN.
Tip: Never Exclude Browsers, Email Clients, Or Download Managers From VPN Tunneling.
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) Enhances Your Online Privacy By Encrypting Your Internet Traffic And Masking Your IP Address. It Protects Your Data On Public Wi-Fi, Hides Browsing Activity From Hackers And ISPs, And Helps Bypass Geo-restrictions. VPNs Also Add A Layer Of Defense Against Malware By Blocking Malicious Websites And Trackers When Using Advanced Features. However, A VPN Does Not Remove Existing Malware Or Act As Antivirus Software. For Full Protection, Combine VPN Use With Antivirus Tools, Regular Software Updates, And Cautious Browsing Habits. Always Choose A Reputable VPN Provider With Strong Security And Privacy Policies.
LuaDream Malware, Remove LuaDream Malware, Uninstall LuaDream Malware, Get Rid Of LuaDream Malware, Delete LuaDream Malware